Widgetized Section
Go to Admin » Appearance » Widgets » and move Gabfire Widget: Social into that MastheadOverlay zone
States like Colorado are setting agenda for county sheriffs working with ICE on mass deportations
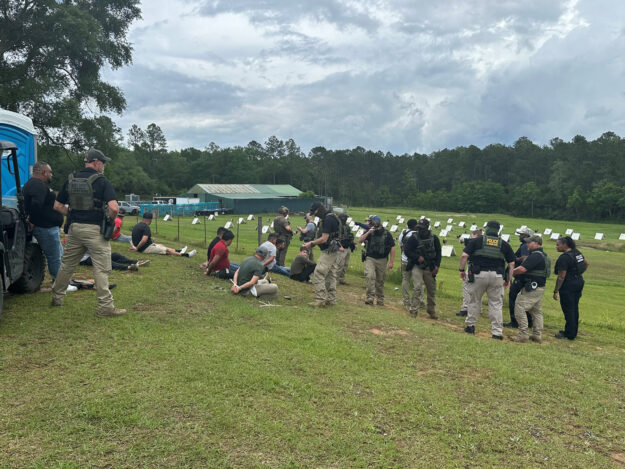

U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement officers, some of them masked, work alongside Harrison County, Miss., sheriff’s deputies to make arrests in an investigation into illegal immigration and cockfighting in early May (ICE photo).
Local sheriffs are on the front lines in deciding whether to participate in the Trump administration’s mass deportation plans. But states increasingly are making the choice for them.
More and more, sheriffs’ hands are tied no matter whether they do — or don’t — want to help with deportations, though they often get the blame when conservatives draw up lists of sanctuary cities.
“‘Naughty lists,’ as we call them, are not super helpful here,” said Patrick Royal, a spokesperson for the National Sheriffs’ Association. “We all know there are places like Colorado where you can’t [help with deportations], and places like North Carolina where you have to.”
Cooperation between sheriffs and U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement lies at the heart of the Trump administration’s immigration detention policy. The administration plans to punish noncooperative jurisdictions with funding cuts — though many legal experts agree that cooperation is voluntary unless state or local laws say otherwise.
Sheriffs, who typically run local jails, must decide what to do when faced with immigration detainers — requests from ICE to hold onto incarcerated people up to two extra days so ICE officers can show up and arrest them. ICE issues those detainers when the agency reviews fingerprints sent electronically for background checks as part of the jail booking process.
Otherwise, arrested suspects who post bond or are otherwise released by a judge might go free despite their immigration status, prompting ICE in some cases to pursue them in the community.
In North Carolina, Sheriff Garry McFadden ran on a platform of limiting cooperation with ICE when he was elected in Mecklenburg County, home to Charlotte, in 2018. But today, McFadden must comply with detainers because of a state law passed last year.
In a now-retracted Facebook post, U.S. Sen. Thom Tillis in late April accused Mecklenburg and several other North Carolina counties of “shielding criminal illegal immigrants” as sanctuary jurisdictions. Tillis, a North Carolina Republican, said in the post he was writing federal legislation to prosecute sanctuary jurisdictions.
“You can’t say we’re a sanctuary county and have state laws that say we have to work with ICE. You can’t have both,” McFadden said. He added that he’d like more choice about whether to comply with detainers. A federal funding cutoff would endanger important jail programs such as rape counseling, he said.
“Everybody’s focused on immigration like that’s the biggest fire, and nobody wants to address the other things. The losers will be the prisoners who need all these services we provide,” McFadden said.
Conservative sheriffs in Democratic-controlled states also can be frustrated by state policy on detainers. Sheriff Lew Evangelidis of Worcester County, Massachusetts, said he’s been criticized for releasing prisoners wanted by ICE but sometimes has no choice: A 2017 state Supreme Court ruling prohibits holding prisoners based on detainers.
“If they [ICE] want this person and consider them a threat to public safety, then I want that person out of my community. I want to keep my community safe,” said Evangelidis. He supported a Republican-sponsored effort in the state legislature to allow 12-hour holds for ICE if a judge determines the prisoner is a threat to public safety, but the amendment was voted down in April.
States act on detainers
Many experts agree that ICE detainers can be legally ignored if states allow sheriffs to do that.
“That detainer request is just that, a request, it’s not a requirement,” said Cassandra Charles, a staff attorney at the National Immigration Law Center, which is opposing Louisiana’s lawsuit to reverse a court-ordered ban on cooperation between Orleans Parish and ICE.
The general counsel for the North Carolina Sheriffs’ Association, Eddie Caldwell, agreed that the detainers are voluntary under federal law.
The association supports a state bill now under consideration that would require not only the 48-hour detention but also a notice sent 48 hours before release to let ICE know the clock is running. The proposal has passed the House.
The notification matters, Caldwell said, because there can be criminal proceedings that take weeks or months, so ICE in many cases doesn’t realize the 48-hour window has started.
Tillis’ office said the senator’s disagreement with McFadden, a Democrat, and other sheriffs is about that notification.
“It’s not necessarily that [sheriffs] are breaking the law, but rather making it as difficult as possible for ICE to take prisoners into custody by refusing to do some basic things. Notification is important,” said Daniel Keylin, a senior adviser to Tillis.
States including California, Colorado and Massachusetts ban compliance with the ICE detainers, on the general principle that it’s not enough reason to hold people in jails when they’re otherwise free to go because of bail or an end to their criminal cases. Those three states have made recent moves to defend or fine-tune their rules.
California’s attorney general also has issued guidance to local jurisdictions based on a 2017 state law limiting cooperation with immigration authorities. That law withstood a court challenge under the first Trump administration.
Colorado has a law against holding prisoners more than six hours longer than required, and a new bill sent to Democratic Gov. Jared Polis last week would specify that even those six hours can’t be for the purpose of an immigration detainer.
Iowa, Tennessee and Texas are among the states requiring cooperation with detainers.
And Florida has gone further, requiring sheriffs to actively help ICE write detainers though official agreements in which local agencies sign up to help enforce immigration laws.
Cooperation boosts arrests
Such cooperation makes a big difference, experts say — jails are the easiest place to pick up immigrants for deportation, and when local sheriffs and police help out, there are more arrests.
“A larger share of ICE arrests and deportations are happening in places where local law enforcement is cooperative with ICE,” said Julia Gelatt, associate director for the Migration Policy Institute’s U.S. Immigration Policy Program, speaking at a recent webinar.
“A declining share of arrests and deportations are happening from places like California, where there are really strict limitations on local law enforcement’s cooperation with ICE,” she added.
ICE is making about 600 immigration arrests daily, twice the rate as during the last year of the Biden administration, said Muzaffar Chishti, an attorney and policy expert at the Migration Policy Institute, speaking at the same event.
Reports on deportations are incomplete, Chishti said, but he estimated the current administration is on track to deport half a million people this year and is trying to get that number higher.
“The Trump administration has not been able to change the laws that are on the books, because only Congress can do that,” Chishti said. “It’s going to take congressional action for the Trump administration to achieve its aim of higher [arrest and deportation] numbers.”
President Donald Trump has added more pressure, last month requesting a list from Attorney General Pam Bondi and Homeland Security Secretary Kristi Noem of sanctuary cities, which he says would face funding cuts. The administration also has sued some states, including Colorado, Illinois and New York, over their policies.
Asked for comment on the legality of funding cutoffs for sanctuary policies, Bondi’s office referred to a February memo in which she promised to “end funding to state and local jurisdictions that unlawfully interfere with federal law enforcement operations.” The memo cites a federal law saying local officials “may not prohibit, or in any way restrict” communication about immigration status.
Local jurisdictions in Connecticut, Minnesota, New Mexico, Oregon and Washington joined a February lawsuit led by the city and county of San Francisco and Santa Clara County in California against a Trump administration executive order calling for defunding cities with sanctuary policies, calling the order “illegal and authoritarian.”
In April, a U.S. district court in California issued a preliminary injunction in that case preventing any funding cutoff over sanctuary policies to the cities and counties in the lawsuit. And on Friday, the federal judge, William Orrick, ruled that the injunction applies to any list of sanctuary jurisdictions the administration may target for funding cuts.
Trump’s new executive order seeking the list cannot be used as “an end run” around Orrick’s injunction, the judge wrote, while he decides the legality of detainer policies and other issues.
“The litigation may not proceed with the coercive threat to end all federal funding hanging over the Cities and Counties’ heads like the sword of Damocles,” Orrick wrote.
Editor’s note: This story first appeared on Stateline, which is part of States Newsroom, a nonprofit news network supported by grants and a coalition of donors as a 501c(3) public charity. Stateline maintains editorial independence. Contact Editor Scott S. Greenberger for questions: info@stateline.org.